Haruko Miura, Matsuda Michiyuki, Kazuhiro Aoki
Laboratory of Bioimaging and Cell Signaling, Graduate School of Biostudies, Kyoto University, Japan; Imaging Platform for Spatio-Temporal Information, Graduate School of Medicine, Kyoto University, Japan
概要・原理
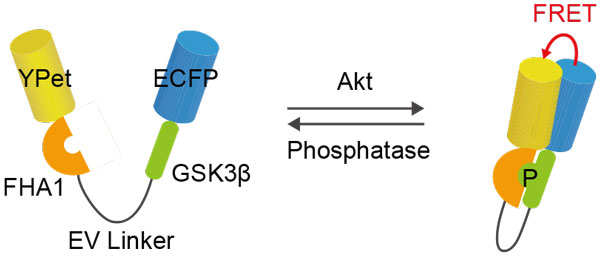
This protocol provides a step-by-step description of time-lapse Förster resonance energy transfer (FRET) imaging by using the specific example of the FRET biosensor Eevee-iAkt (Miura et al., 2014). Eevee-iAkt is a genetically encoded FRET biosensor for the visualization of the spatiotemporal dynamics of Akt activity in living cells. As an intramolecular FRET biosensor, Eevee-iAkt comprises, starting from the N-Terminus, YPet as FRET donor, the phosphopeptide-binding domain FHA1, a substrate sequence derived from the Akt substrate GSK3β, ECFP as FRET acceptor, and a nuclear export sequence. Phosphorylation of the substrate sequence by Akt leads to a conformational change due to binding of the FHA1 domain to the phosphorylated substrate sequence, leading to an increase in the FRET efficiency (Figure 1).
装置・器具・試薬
Equipment
•Inverted fluorescence microscope (IX-81, Olympus)
•CCD camera (CoolSNAP-K4, Roper Scientific)
•LED illumination system (CoolLED precisExcite, Molecular Devices)
•Laser-based autofocusing system (IX2-ZDC, Olympus)
•Automatic programmable XY stage (MD-XY30100T-Meta, SIGMA KOKI)
•Optical filters for dual emission imaging (XF1071 440AF21 excitation filter, XF2034 455DRLP dichroic mirror, XF3075 480AF30 emission filter for CFP, XF3079 535AF26 emission filter for FRET, all from Omega Optical)
•60x oil-immersion objective lens (UPlanSApo 60x/1.40 oil, Olympus)
•35 mm glass bottom dish (Asahi Techno Glass)
•Metamorph software (Universal Imaging)
•Excel software (Microsoft)
Reagents
•Mammalian expression plasmid encoding Eevee-iAkt. This probe is available from the Aoki laboratory upon request.
•293fectin (Invitrogen)
•Bovine serum albumin (BSA) (Sigma Aldrich)
•Phenol red-free M199 (Invitrogen)
•Epidermal growth factor (EGF) (Sigma Aldrich)
•HeLa cells
詳細
- Sample preparation
- Plate HeLa cells on a 35 mm glass base dish and let cells grow for one day at 37°C, 5% CO2.
- Transfect cells with 1 μg plasmid DNA encoding Eevee-iAkt using 293fectin according to manufacturer’s instructions.
- Culture transfected cells for 1 to 2 days at 37 °C, 5% CO2.
- FRET time-lapse imaging
- Starve cells in 2 ml M199 medium 20 mM HEPES 0.1% BSA for 3 hours.
- Transfer 500 μl of the conditioned medium to a microtube and add EGF (final concentration 10 ng/ml).
- Set up the microscope and pre-warm the imaging chamber to 37 °C, and place the glass bottom dish onto the stage.
- Focus cells, set the autofocus, and select around 5 positions with cells expressing the FRET biosensor.
- Wait for 1 to 2 minutes to allow the YFP to recover from reversible photo-bleaching and then start image acquisition.
- After 10 minutes pause image acquisition, add the EGF containing conditioned medium to the dish, and resume image acquisition for further 30 minutes. Note: Do not touch the dish!
- Data processing
- Subtract background from each plane of the image stack file.
- Create FRET/CFP ratio images in the intensity modulated display (IMD) mode.
- Export background subtracted FRET and CFP intensities of single cells to Excel software.
- Average the intensities over the cell area, calculate the FRET/CFP ratio, and normalize to the average FRET/CFP ratio before stimulation.
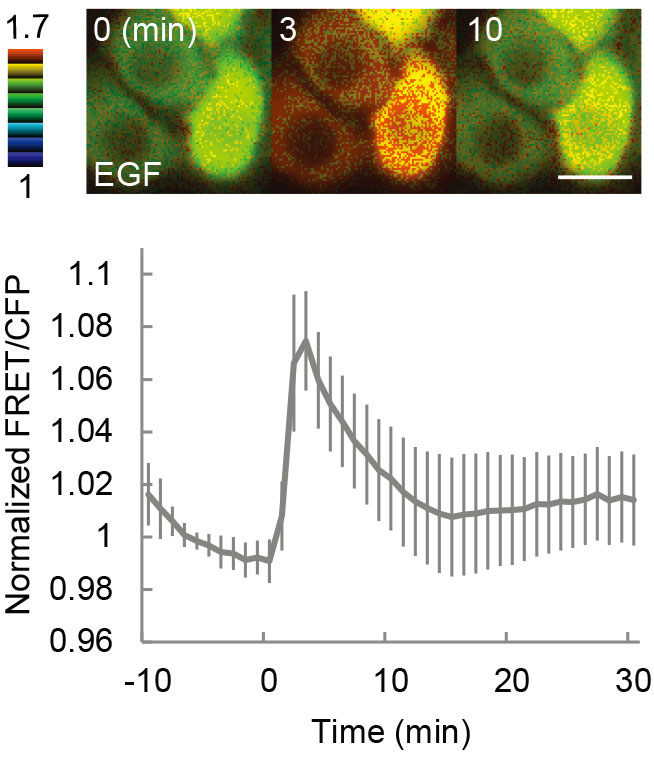
- Plot the FRET/CFP ratio versus elapsed time. Typical results are shown in Figure 2.
工夫とコツ
•Procedures for the preparation of intramolecular FRET biosensors were previously described by Komatsu et al. (2011).
•Details on FRET image acquisition and processing and related journals for Metamorph software are provided by Aoki and Matsuda (2009).
参考文献
Miura, H., Matsuda, M., and Kazuhiro A. (2014). Development of a FRET biosensor with high specificity for Akt. Cell Struct Funct. 39, 9-20. Komatsu, N., Aoki, K., Yamada, M., Yukinaga, H., Fujita, Y., Kamioka, Y., and Matsuda M. (2011). Development of an optimized backbone of FRET biosnesors for kinases and GTPases. Mol Biol Cell. 22, 4647-56. Aoki, K. and Matsuda M. (2009). Visualization of small GTPase activity with fluorescence resonance energy transfer-based biosensors. Nat Protoc. 4, 1623-31.



